Setareh Keyhani Wrote In a Note To The International Relations Think Tank :Geopolitics is briefly called the analysis of geographical influences on power relations in international relations. The term geopolitics was first coined by the Swedish political scientist Rudolf Cologne in the late twentieth century, and its use spread throughout Europe between the First and Second World Wars and was used globally in the second period.
Written by: Setareh Keyhani British Studies MA Student, Faculty of World Studies (FWS), University of Tehran
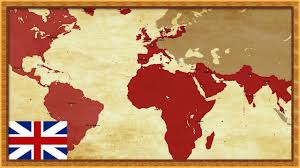
IRTT: Britain is a country by a limited geographical location but very powerful and influential over other countries. From time immemorial to the present day, Britain has been one of the world’s superpowers. A small country with 54 colonies (Commonwealth countries) that it colonised over different periods. A review of history books and past events reveals one of the main reasons for Britain’s desire to expand its land border, is its geographical location. Britain’s geopolitical issues have always been outside its geographical boundaries, and it is the same today. Great Britain is located off the north-western coast of continental Europe and lies between the North Atlantic and the North Sea and comes within 35 kilometres of the northwest coast of France, from which it is separated by the English Channel. Britain’s geographical location has had a significant impact on the formation of foreign relations with EU countries, as well as the rise of power in the Middle East. Britain, is an island on the Atlantic coast, between Ireland and France.
One of the most influential people in increasing British power is Helford Mackinder (1861 – 1947) who was a British political geographer well known for his hypothesis of the rise of Eurasian “heartland” and the support “maritime lands” including the other continents. His theory “heartland” had a great influence on the creation of geopolitical debates and the relationship between geography and politics and foreign policy as well. The impact of his theories on British foreign policy from the past to the present cannot be denied. Not only did it increase British power in the region, but it also gave rise to power in the Middle East.
The most important variables influencing the creation of Mackinder’s theory as well as British global policies include the variables of territorial position, power, geopolitical determinism and geopolitical rivalries.
The British Isles’ position kept the country safe from enemy occupation during World Wars I and II, but at the same time isolating the country from Europe.
According to Halford Mackinder’s theory in 1904, the territorial constraints and geopolitical constraints of Britain and the influence of the position of the “marginal land” on its relations with Europe and the world. Therefore, Britain has sought to expand its territory to strengthen its island position. In a nineteenth-century European perspective, the size of the territory was very important. This means that the larger a country is, the more its political power and civilisation will develop.
The British had two strategic concepts and perceptions of power: first, central and national power, and second, international power. This power has been considered by geopoliticians in the military, naval, land, air and space spheres. Throughout history, gaining ground has been an incentive for the British to increase their power.
The British needed to annex the island’s neighbouring areas to strengthen their dominance and influence over Europe and beyond. From the alliance of England with Scotland, a single country called the United Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, as a result of which this territorial alliance of England could increase its political and economic power in Europe and overseas.
The British needed to annex the island’s neighbouring areas to strengthen their dominance and influence over Europe and beyond. From the union of England with Scotland, a single country called the United Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, as a result of which this territorial alliance of England could increase its political and economic power in Europe and overseas.
Geopolitical algebra in international relations is the position of environmental, geographical, climatic and territorial factors in determining the sphere of influence of countries. The pressure of geographical determinism forced Britain to choose a policy of isolation in its relations with European powers. Instead, focus on distant lands for presence and influence in India, which has affected its relations with Europe. Thus, the territorial position of this country and its concern for the preservation of the empire outside Europe were much more important, than to devote its resources to the war with European powers such as France, Germany and Spain.
The famous saying during the reign of Queen Victoria that “the sun never sets in the British Empire” refers to the issue of territorial development and its relation to the British geopolitical power outside Europe, ie distant lands in Africa, America and Asia.
Consequently, the influence of geography on a country’s political decisions and its foreign relations cannot be denied. It can therefore be concluded that negative geographical determinism has led to the expansion and empowerment of Britain. Britain used its poor geographical conditions to expand its borders and become a superpower. It showed how powerful and manageable Britain is. Now a question arises why Iran could not expand its power despite positive geographical determinism?


